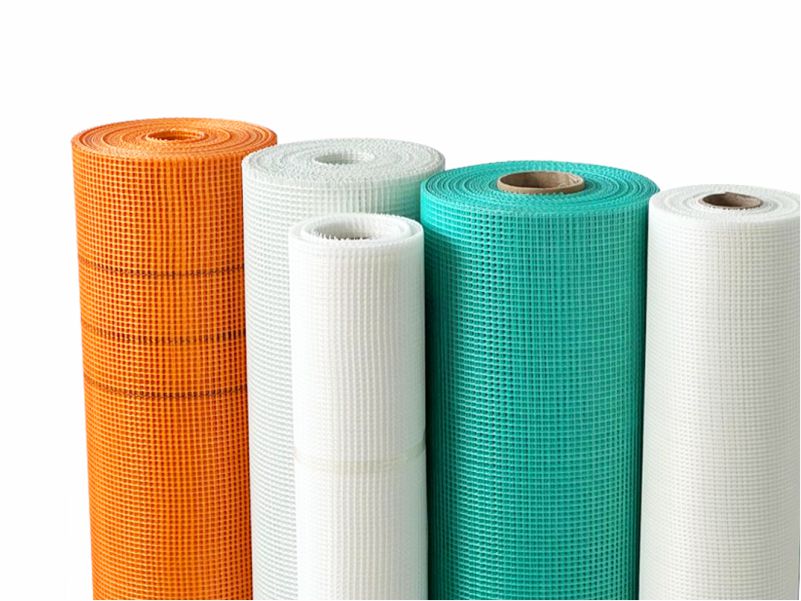
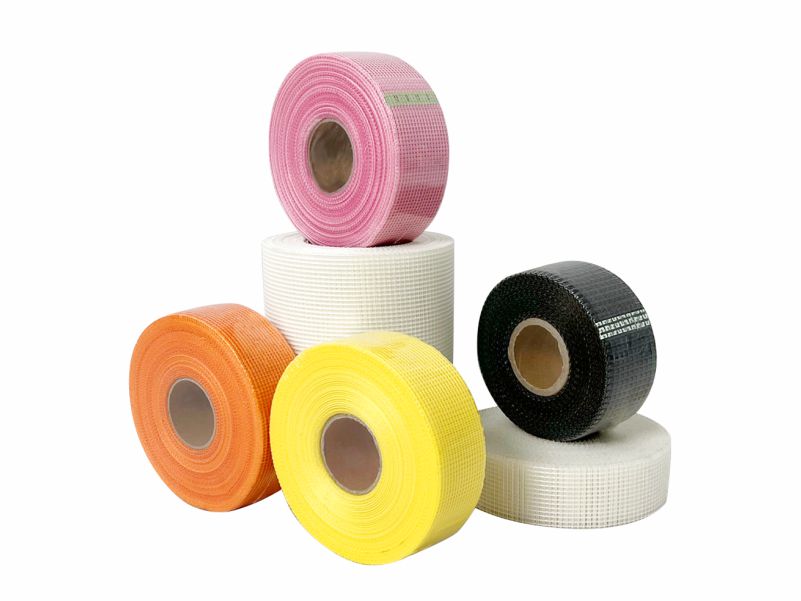
Fiberglass is a crucial industrial material known for its high strength, corrosion resistance, heat resistance, low density, good insulation properties, and relatively low cost. It is widely used in construction, automotive, wind power generation, electronics, and aerospace sectors. With the continuous development of the global economy and technology, the future market prospects for the fiberglass industry are very promising.
1. Growing Market Demand
- Construction and Infrastructure: With the acceleration of global urbanization, especially in emerging markets, the demand for fiberglass in the construction sector is steadily increasing. This includes applications in insulation systems, wall reinforcement, road and bridge engineering, and more. Additionally, many countries are promoting energy-efficient and green building policies, further driving the widespread use of fiberglass materials.
- Transportation: Fiberglass is widely used in automotive manufacturing due to its lightweight properties, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and reduced carbon emissions. In the aerospace sector, fiberglass-reinforced composites are increasingly being used in aircraft and drones due to their strength and durability.
- Renewable Energy: The wind power industry is a major market for fiberglass composites, with wind turbine blades typically made from fiberglass-reinforced materials. The rapid growth of the wind energy sector, driven by the increasing demand for renewable energy, presents significant growth opportunities for the fiberglass industry.
2. Technological Advancements Driving Industry Growth
- Composite Material Technology: With advancements in material science, the composite technologies combining fiberglass with other materials are continuously innovating. Fiberglass-reinforced composites offer higher strength, durability, and lightweight performance, making them increasingly applicable across various industries. These composites have become vital in modern industries, especially in high-tech sectors like aerospace, aviation, and automotive.
- Production Process Improvements: Continuous improvements in fiberglass production processes and increased automation help reduce production costs, improve product quality, and enhance efficiency. Green and eco-friendly production techniques, such as reducing energy consumption and waste during manufacturing, are becoming a focus for future development.
3. Policy Support and Environmental Trends
- Environmental Protection and Sustainability: Governments around the world are increasingly emphasizing environmental protection and sustainable development. Fiberglass, as a recyclable and eco-friendly material, aligns with the demands of the future green economy. For example, regulations in the European Union and the United States that mandate energy efficiency in buildings are likely to drive the use of fiberglass materials in energy-efficient construction.
- Policy-Driven Industry Development: Many national governments are offering policy incentives and financial support to promote green technologies and improve energy efficiency. These policies are spurring the adoption of fiberglass in renewable energy sectors (e.g., wind power) and lightweight transportation solutions.
4. Globalization and Market Competition
- Global Expansion: The fiberglass market is experiencing globalization, with increasing industrialization and infrastructure development in emerging markets. Fiberglass manufacturers are expanding their global production and sales networks, creating new opportunities while also intensifying industry competition.
- Market Consolidation and Innovation: With the diversification of market demand and rising competition, fiberglass companies need to pursue mergers, technological innovation, and product upgrades to stay competitive. Some large fiberglass manufacturers are acquiring new technology companies or expanding their product lines to strengthen their market positions.
5. Challenges and Responses
- Raw Material and Energy Price Volatility: Fiberglass production relies on raw materials such as glass and sand, as well as energy sources like natural gas and electricity. Fluctuations in these prices can affect industry profit margins. The sector must improve energy efficiency, optimize supply chains, and innovate processes to mitigate these challenges.
- Environmental Regulation Pressure: Despite its environmentally friendly characteristics, fiberglass production can still have some environmental impacts. With increasingly stringent environmental regulations, companies need to reduce emissions and enhance their green technologies during production to meet future regulatory standards.
Conclusion
The fiberglass industry has broad prospects for future growth, particularly in expanding applications in construction, transportation, renewable energy, and high-tech industries. Technological advancements, policy support, and globalization offer significant opportunities. However, the industry also faces challenges such as volatile energy prices and stricter environmental regulations. By focusing on technological innovation, green production, and market expansion, the fiberglass industry is expected to maintain sustainable growth in the future.